Gastroesophagul Reflux Disease
In gastroesophageal reflux disease, stomach contents, including acid and bile, flow backward from the stomach into the esophagus, causing inflammation in the esophagus and pain in the bottom of the chest.
-
Reflux occurs when the ring-shaped muscle that normally prevents the contents of the stomach from flowing back into the esophagus (called the lower esophageal sphincter) does not function properly.
-
The most typical symptom is heartburn (a burning pain behind the breastbone).
-
The diagnosis is based on symptoms and sometimes esophageal pH testing.
-
The first treatment is avoiding trigger substances (such as alcohol and fatty foods) and taking drugs that reduce stomach acid, but, if these methods fail, doctors sometimes do surgery.
The esophagus is the hollow tube that leads from the throat (pharynx) to the stomach. The lower esophageal sphincter is the ring of muscle that holds the bottom of the esophagus closed so that food and stomach acid do not flow back up the esophagus. When people swallow, this sphincter normally relaxes to allow food into the stomach.
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is common. It occurs in 10 to 20% of adults. It also occurs frequently in infants, sometimes beginning at birth (see Gastroesophageal Reflux in Children).
The stomach lining protects the stomach from the effects of its own acid. Because the esophagus lacks a similar protective lining, stomach acid and bile that flow backward (reflux) into the esophagus may cause symptoms and in some cases damage.
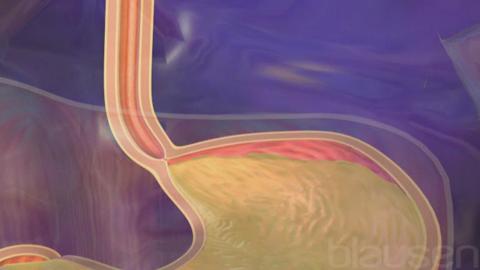 Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
Acid and bile reflux into the esophagus when the lower esophageal sphincter is not functioning properly. When a person is standing or sitting, gravity helps to prevent the reflux of stomach contents into the esophagus, which explains why reflux can worsen when a person is lying down. Reflux is also more likely to occur soon after meals, when the volume and acidity of contents in the stomach are higher and the sphincter is less likely to work properly. Factors contributing to reflux include
-
Weight gain
-
Fatty foods
-
Caffeinated and carbonated beverages
-
Alcohol
-
Tobacco smoking
-
Certain drugs
Types of drugs that interfere with lower esophageal sphincter function include those that have anticholinergic effects (such as many antihistamines and some antidepressants), calcium channel blockers, progesterone, and nitrates. Delayed emptying of the stomach (for example, due to diabetes or use of opioids) can also worsen reflux.
Symptoms
Heartburn (a burning pain behind the breastbone) is the most obvious symptom of gastroesophageal reflux. Heartburn may be accompanied by regurgitation, in which the stomach contents reach the mouth. If stomach contents reach the mouth, they sometimes cause sore throat, hoarseness, cough, or a sensation of a lump in the throat (globus sensation). Sometimes, stomach contents trickle into the lungs, causing cough and/or wheezing. People who have longstanding heartburn sometimes develop difficulty swallowing (dysphagia).
Complications of gastroesophageal reflux
Prolonged exposure of the lower part of the esophagus to repeated reflux may cause
-
Inflammation of the esophagus (esophagitis)
-
Ulcers (open sores) of the esophagus (erosive esophagitis)
-
Narrowing of the esophagus (esophageal stricture)
-
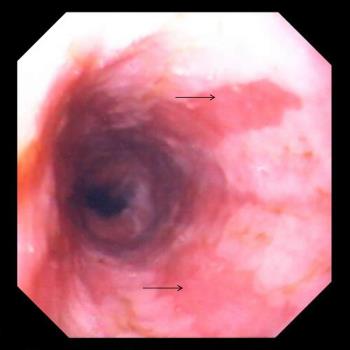
Abnormal cells in the esophagus that may become cancerous
Inflammation of the esophagus (esophagitis or erosive esophagitis) causes symptoms typical of GERD but perhaps more severe. It also may cause pain with swallowing (odynophagia). Some people have bleeding that is usually slight but can be massive. The blood may be vomited up or may pass through the digestive tract, resulting in the passage of dark, tarry stools (melena) or bright red blood, if the bleeding is heavy enough. Mild bleeding over a long period of time can cause iron deficiency anemia.
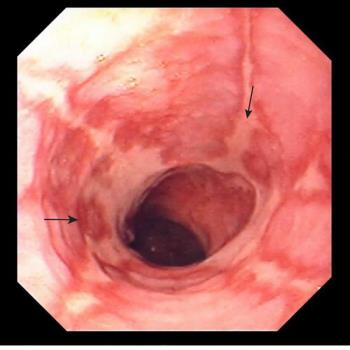
Esophagitis Caused by Gastroesophageal Reflux
Esophageal ulcers are open sores on the lining of the esophagus. They can cause chest pain upon swallowing that is usually located behind the breastbone or just below it, similar to the location of heartburn.
Narrowing (stricture) of the esophagus caused by reflux makes swallowing solid foods increasingly more difficult.
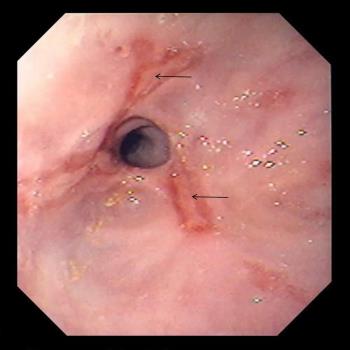
Narrowing (Stricture) of the Esophagus
Prolonged irritation causes the cells lining the esophagus to change, which results in a condition called Barrett esophagus.
Changes may occur without symptoms. These abnormal cells are precancerous and can sometimes progress to cancer.
Diagnosis
- Endoscopy with biopsy
- Sometimes pH testing
- Sometimes manometry
When symptoms point to the diagnosis of GERD, treatment can be started without testing. Testing is usually reserved for situations in which the diagnosis is not clear, treatment has not controlled symptoms, or symptoms have been present for a long time.
When testing is needed, the first test is usually to examine the esophagus using a flexible viewing tube (endoscopy). Endoscopy is the best test for diagnosing esophagitis, erosive esophagitis, esophageal ulcer, esophageal strictures, esophageal cancer, and Barrett esophagus. During endoscopy, doctors may remove tissue for examination under a microscope (biopsy).
If endoscopy and biopsy results are normal in people whose symptoms are very suggestive of GERD, doctors may do esophageal pH testing (pH is a measure of acidity). In this test, a thin, flexible tube with a sensor probe on the tip is placed through the nose and into the lower esophagus. The tube stays in place for 24 hours. The other end of this tube is attached to a monitor that is worn by the person. The monitor records the acid levels in the esophagus, usually for 24 hours. Besides determining how much reflux is occurring, this test identifies the relationship between symptoms and reflux. This test is also helpful for people who have symptoms that are not typical of reflux. The esophageal pH test is suggested for all people being considered for surgery to correct gastroesophageal reflux. People who cannot tolerate a tube in their nose can have a small pH capsule attached to the lower part of their esophagus.
Pressure measurements at the lower esophageal sphincter using a test called manometry indicate the function of the sphincter and can distinguish a normal sphincter from a poorly functioning one. The information gained from this test helps the doctor decide whether surgery is an appropriate treatment.
Prevention
Several measures may be taken to relieve gastroesophageal reflux:
- Raising the head of the bed
- Avoiding drugs and foods that cause symptoms or stimulate acid
- Not eating before bedtime
- Losing weight
Raising the head of the bed about 6 inches (about 15 centimeters) can help prevent acid from flowing into the esophagus as a person sleeps. Drugs that cause symptoms should be avoided, as should smoking. Coffee, alcohol, fatty foods, acid-containing beverages such as orange juice, cola drinks, vinegar-based salad dressings, and other substances that strongly stimulate the stomach to produce acid or that delay stomach emptying should be avoided as well. People should avoid eating 3 hours before bedtime. People who are overweight and those who have gained weight recently should lose weight.
Treatment
- Proton pump inhibitors or sometimes histamine-2 blockers
- Dilation of narrowed areas
- Fundoplication
- Management of Barrett esophagus
Proton pump inhibitors, the most powerful drugs for reducing stomach acid production, are usually the most effective treatment for gastroesophageal reflux and for esophagitis and erosive esophagitis due to gastroesophageal reflux. Healing typically requires taking the drugs for a 4- to 12-week period. These drugs may be continued long-term, but if this is necessary, doctors try to use a lower dose. Alternatives to proton pump inhibitors include histamine-2 (H2) blockers and drugs that stimulate the movement of contents through the esophagus, stomach, and intestines (called promotility drugs). However, these drugs are not as effective as proton pump inhibitors.
Esophageal narrowing is treated by repeatedly dilating the narrowed area using balloons or tubes. If dilation is successful, narrowing does not seriously limit what a person can eat.
Barrett esophagus rarely disappears after use of a proton pump inhibitor and typically remains unchanged. If the cells become precancerous, treatment options that can be done during endoscopy include methods that destroy the abnormal tissue using radio waves (radiofrequency ablation), extreme cold (cryotherapy), or a laser beam (laser ablation). Alternatively, the tissue may also be surgically removed. However, abnormal cells may still remain even after treatment relieves symptoms. Therefore, people with Barrett esophagus are asked to undergo an endoscopic examination periodically to ensure that the condition is not progressing to cancer.
Surgery is an option for treatment of gastroesophageal reflux for people whose symptoms are not relieved by drugs or for people who have ulcers, bleeding, or esophagitis that persists even after symptoms are relieved. In addition, surgery may be the preferred treatment for people who do not like the prospect of having to take drugs for many years. A minimally invasive procedure done through a laparoscope (called fundoplication) is available. However, 20 to 30% of people who undergo this procedure have side effects, most commonly difficulty swallowing and a feeling of bloating or abdominal discomfort after eating.





